In an ever-evolving world, the importance of inclusive play cannot be overstated. For children with hearing impairments, the concept of audism—prejudice or discrimination against individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing—can create barriers to engaging and meaningful play experiences. Magnetic blocks, with their versatile and inclusive nature, offer an excellent solution to foster inclusive play for audism children. In this blog, we explore how magnetic blocks can support deaf and hard-of-hearing (DHH) children and contribute to a more inclusive play environment.
Understanding Audism and Its Impact on Play
Audism can manifest in various ways, from societal biases to lack of accessible resources. For DHH children, these barriers can limit their opportunities for interactive and stimulating play, which is crucial for cognitive and social development. Inclusive play environments are essential to counteract these limitations, providing DHH children with the same opportunities for growth and learning as their hearing peers.
The Benefits of Magnetic Blocks for DHH Children
Magnetic blocks are a fantastic tool for creating inclusive play environments. Here are some of the key benefits they offer:
-
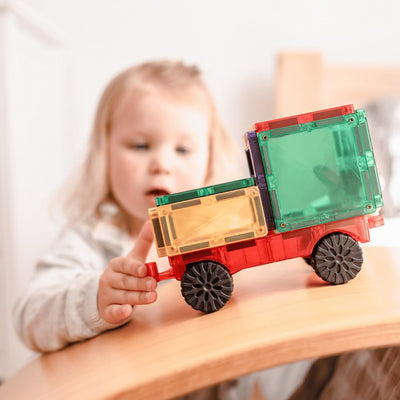
Tactile and Visual Engagement: Magnetic blocks are highly tactile, making them ideal for hands-on learning. Their bright colors and varying shapes provide strong visual stimuli, which are particularly beneficial for DHH children who rely more on visual cues.
-
Promoting Fine Motor Skills: As children manipulate magnetic blocks, they enhance their fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination. This is crucial for all children, including those who are DHH, as it supports overall physical development.
-
Encouraging Creativity and Imagination: Magnetic blocks allow children to build and create various structures, fostering creativity and imagination. This type of play encourages problem-solving and critical thinking, important skills for all children.
-
Facilitating Communication: Magnetic blocks can serve as a medium for communication. DHH children can use them to express ideas and stories visually, bridging the gap between different communication modes.
Strategies for Using Magnetic Blocks to Support DHH Children
To maximize the benefits of magnetic blocks for DHH children, consider incorporating the following strategies into playtime:
-
Interactive Storytelling: Use magnetic blocks to create characters and scenes, encouraging DHH children to tell stories visually. This can enhance their narrative skills and boost their confidence in communication.
-
Collaborative Play: Encourage group activities where DHH children can work with their hearing peers to build structures. This fosters teamwork and social interaction, promoting an inclusive environment.
-
Incorporating Visual Aids: Combine magnetic blocks with visual aids, such as picture cards or sign language flashcards, to reinforce learning concepts and vocabulary.
-
Creating Themed Challenges: Design themed building challenges that require DHH children to think critically and creatively. Themes can range from constructing animals to building dream houses, providing endless possibilities for engagement.
Creating an Inclusive Play Space
For parents and educators looking to create an inclusive play space, here are some tips:
-
Ensure Accessibility: Make sure that magnetic blocks and other play materials are easily accessible to all children. Organize the play area to accommodate various needs and preferences.
-
Use Visual Instructions: Provide visual instructions and demonstrations for activities involving magnetic blocks. This helps DHH children understand the tasks and participate fully.
-
Encourage Peer Support: Foster an environment where children are encouraged to help and support each other. Peer support can enhance the learning experience and promote inclusivity.
Real-Life Success Stories
Numerous parents and educators have shared success stories of how magnetic blocks have positively impacted the play experiences of DHH children. For instance, one parent noted that their child became more confident and communicative after regularly playing with magnetic blocks, using them to create intricate structures and share stories with family members. An educator highlighted how magnetic blocks helped integrate DHH children into group activities, fostering a sense of belonging and collaboration.
Conclusion
Magnetic Blocks are more than just toys; they are powerful tools for creating inclusive play environments that support the development and well-being of DHH children. By embracing the tactile, visual, and collaborative nature of magnetic blocks, parents and educators can help dismantle the barriers imposed by audism and ensure that every child has the opportunity to learn, play, and grow in an inclusive and supportive setting.